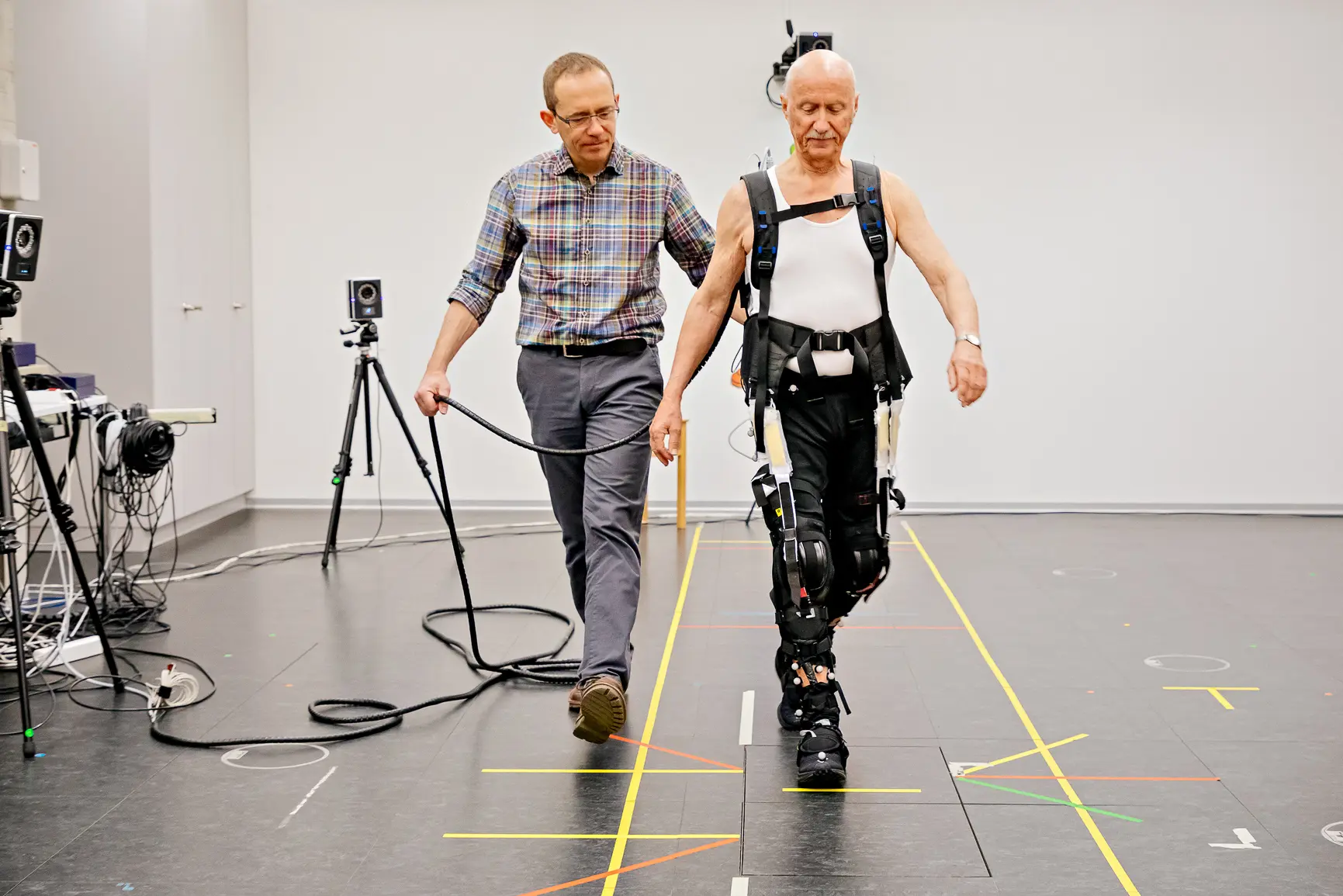
amicitaacademy.com – The emergence of pediatric soft exoskeletons marks a significant advancement in rehabilitation technology, supporting independent mobility for children with motor impairments. A recent breakthrough is the “MyoStep” suit, developed collaboratively by the University of Houston’s NSF BRAIN Center and TIRR Memorial Hermann. This soft, smart-material-based exoskeleton utilizes artificial muscles, smart fabrics, and a network of sensors to adapt to a child’s growth and needs, vastly improving usability compared to rigid frames. Designed to be lightweight and discreet, MyoStep allows children with cerebral palsy to walk more naturally and participate in daily activities with greater ease and confidence.
Meanwhile, advancements in adult rehabilitation continue to accelerate. At CES 2025, Hypershell’s Carbon X hip exoskeleton received a “Best of Innovation in Robotics” award. This device enhances hiking and exercise by supplementing hip movement with carbon-fiber assistance. In parallel, research teams at UMass Amherst showcased a low-profile hip exoskeleton at ICRA 2025 designed for both walking and running, bringing lightweight assistive robotics closer to real-world applications. These systems epitomize a growing trend: exoskeletons that seamlessly augment human motion in everyday environments, not just clinical settings.
Market forecasts underscore this trend, projecting the wearable robotics market to expand from US $2.49 billion in 2025 to $30.56 billion by 2032, at a compound annual growth rate of over 43%. Growth is fueled by demand in healthcare, occupational safety, and fitness sectors. Soft, biomimetic suits like those produced by South Korea’s Hurotics are also gaining attention; their H‑Flex suit, emphasizing customization and wearability, recently won international innovation awards.
These developments highlight how exoskeletons are evolving from heavy, clinical apparatuses to adaptable, user-centric wearables. By blending biomechanics with smart materials and sensors, next-gen exoskeletons are poised to empower individuals across all ages and abilities. As research and commercialization progress, these technologies promise to redefine mobility support in rehabilitation, daily life, and beyond.